Articles
How to choose optimum PC computer specs for homerecording
- Foreword
- Desktop or laptop?
- CPU
- MB
- RAM
- HDD/SSD
- GPU
- Expansion cards
- PSU
- Case
- Examples
- Glossary
- Further reading
- Related articles
Foreword
You can build your own custom PC, lots of companies build PCs and sell them. There's a huge variety of possible hardware configurations and basically just one operating system to handle them. Then there are also different audio interfaces with their drivers and music production programs. What's great is that you can get a random PC and there's a big chance that it'll work with your DAW and your interface. This article is for those who want to get serious about recording and producing music at home and are planning building or upgrading a PC.
Back to topDesktop vs laptop
If performance is what you want, go for a desktop. These are easy to repair, upgrade and you can disable all CPU energy saving capabilities in BIOS/UEFI. It's quite easy to build your own custom PC. Less expensive, more reliable, more powerful.
If mobility is what you're after, go for a laptop. With these it's possible to upgrade HDD, often RAM and in some cases CPU. It's difficult if not impossible with some models to disable processor throttling entirely because cooling systems in laptops are less efficient. Modern notebooks don't have power supply grounding and that's not good for plugging the guitar to an USB powered audio interface - there's more noise. Delicate chassis parts, like hinges, are vulnerable to damage. Remember that leaning forward with hunched shoulders for long hours never does anything good for your health. It's good to have a laptop for recording rehearsals and live performances and a desktop for everyday's work. More expensive, less ergonomic, less reliable, less powerful, but portable.

Desktop PC computer based DAW
Back to topCPU
This is the most important computer component and you should get the best CPU that you can afford. Most CPUs have many cores but single core performance matters as well.
People used to look at processor clock speed. That doesn't really tell you much about performance, however it can tell if the CPU is whether old or designed for low power consumption and heat generation if its clock speed is less than 2GHz. Of course low power consumption is a good thing in laptops, because it allows a laptop to run longer on battery power.
Turbo Boost and Hyper Threading are not usually recommended for audio production, it's usually possible to disable both in BIOS/UEFI.
To get the most of your CPU it's best to disable all energy saving capabilities of the CPU. For an Intel these include SpeedStep, EIST (Enhanced Intel Speed Step), C-States. With AMD disable the Cool & Quiet. It so happens that when you disable processor throttling in a laptop it reduces its clock speed to maintain low heat generation. In such a laptop it's better not to disable such features. Open Hardware Monitor (free) lets you monitor actual CPU speed as well as lots of other parameteres.
Use www.cpu-boss.com to compare processors and find the best CPU for you
Intel Pentium Dual Core T3100 mobile CPU
CPU cooler
Upgrading the cooler that came with the CPU with a better one makes the PC more quiet. Good coolers are big and have replaceable fans.

Intel Core i5-4570 cooler
Back to topMB
Make sure that the mainboard is well suited for other components and it has enough IOs and expansion slots for your needs. Choose one with at least few USB ports and expansion slots. USB ports are sometimes shared and that's bad for low latency performance of USB audio interfaces. You want to have options for upgrade. If you want to overclock both mainboard and processor have to support it. The processor should be unlocked and the mainboard should be able to change the CPU multiplier.
Back to topRAM
- If there's not enough memory in your computer, its performance suffers
- If there's more than enough memory in your PC, then not all of it is being used
- If you want like using virtual instruments, 8GB is a safe starting point, but 4GB is also usable
- If you're bulding your own PC, remember that RAM speed and type should be suited to the memory controller which is a part of the CPU or the MB
- DIMMs are for desktops, SODIMMs are for laptops
- Dual Channel operation boosts memory performance just a little bit, it requires two memory modules that have the same specs installed in appriopriate memory slots. There are also some Intel processors that have Triple Channel and Quad Channel memory controllers
- CL is CAS (Column Address Strobe) Latency, in general lower is better, choose modules with lowest possible CAS Latency
- They say it makes sense to disable system swap file if you have lots of RAM, but it depends on your software and remember that without it programs can crash when there's no more memory left; from my experience it's not worth it
- XMP is Intel Extreme Memory Profile that allows you to overlock the memory if your mainboard supports XMP profiles
- ECC is Error Code Correction, ECC memory modules are designed for server computers and memory controller has to support this feature (Intel Xeon processors support ECC)

DIMM DDR3 1600MHz 4GB Kingston HyperX Black

SODIMM DDR3 1333MHz 1GB Samsung
Back to topHDD/SSD
It's good to have two seperate hard drives for operating system and music production. Typical hard drives are fine, watch out for anything GREEN because that's probably an energy saving product that could give you a headache.
Good SSD drives make your system and apps load much faster so it's good to have one. Movie editing benefits from SSDs as well. Be careful, low budget solutions don't perform that great. The fastest SSDs are PCIe.
Use www.ssdboss.com to compare SSDs and find the best Solid State Drive for you
I don't recommend SSDs for recording songs. Their cells have limited number of times it can be written and erased and recording songs shortens their life.

Western Digital Blue 1.0TB HDD
RAID
RAID can combine multiple drives to one logical unit to improve performance or for data safety reasons. Building a RAID with multiple SSDs can make a dramatic difference in system performance.
Back to topGPU
There were days when GPU didn't matter when you were recording, but today it seems to be a different story.
Integrated vs seperate
Integrated graphics are good enough for most purposes. These are usually a part of the CPU or the mainboard and have no memory of their own.
Graphics cards accelerate movie rendering. This depends on movie production software, but most of these take advantage of NVIDIA CUDA, AMD Accelerated Parallel Processing and Intel Quick Sync Video that some Intel processors support. Don't count on this kind of acceleration if you're using Radeon HD6450 or GeForce GT610, but powerful seperate graphics cards do make a difference here.
In terms of performance seperate doesn't necessarily mean faster, modern CPU integrated graphics are getting better and better. Read benchmark results and use websites like www.gpu-boss.com to compare GPUs.
Windows 8 uses graphics card to accelerate almost everything, making decoding and rendering images faster and improving text performance.
Hardware accelerating everything: Windows 8 graphics on blogs.msdn.com
From my experience graphics cards with memory of their own improve low latency performance, at least in Windows 8. With low budget CPU and GPU (Pentium G3220, Geforce GT610) I could play through plugins without pops and cracks using Focusrite PRO 14 at its lowest latency setting (3.75ms RTL!). That was not the case without the GT610. I had to upgrade the computer with Intel Core i5-4570 to make it work without the GT610.
Use www.gpu-boss.com to find the best graphics card for you
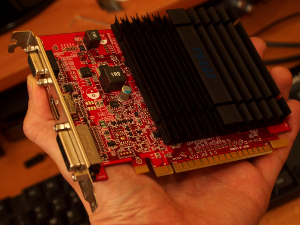
MSI HD6450 with passive cooling
VGA/DVI/HDMI/DisplayPort
DisplayPort, DVI and HDMI are digital, VGA is analog. DVI and HDMI use HDCP and to me everything sounds better and more natural when I use the old analog connection. Both recording and playback. You can call me crazy, but that's how I hear it. I performed some blind tests on friends and those only confirmed that statement. Most people use HDMI/DVI and don't care and perhaps that's the way to go. If you're using a laptop or an AIO computer with no external displays, this proably doesn't matter.
The word has it that digital equals better picture quality, but with high quality shielded VGA cables I can't see the diference.


Low quality (left) and high quality shielded (right) VGA cables
Passive?
Low performance graphics cards often use passive cooling and that's a good thing especially if you want your PC to be quiet.
DPC - NVIDIA vs AMD vs Intel
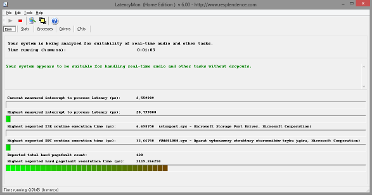
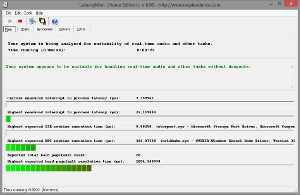
DPC stands for Deffered Procedure Call and it's a mechanism in Windows that allows high priority tasks to postpone other tasks for later execution. Graphic cards drivers can cause high DPC routine execution times and that's not good for low latency audio performance. NVIDIA graphics drivers seem to cause higher DPC than AMD and Intel drivers, ranging from 100µs to 400µs and depending on the GPU model. This doesn't seem to affect low latency performance a lot. AMD graphics drivers behave better and their DPC spikes are equal to those generated by Intel HD Graphics drivers (no more than 15µs). I used AMD HD5450, HD6450, NVIDIA GT610 and GT650 for DPC tests. I also had an opportunity to check DPC on a PC with GeForce 8800GT in Windows 7 and it was 100µs. Driver version doesn't seem to matter here.
LatencyMon results, left: AMD HD5450, right: NVIDIA GT610; Windows 8, Intel Pentium G3220
With LatencyMon by Resplencence you can analyze your system:
Check out LatencyMon by Resplendence
Back to topExpansion cards
Both desktops and laptops can be upgraded with expansion cards.
Desktop - PCI vs PCIe
PCIe is the new standard, PCI is still in use. The names are almost the same, but in fact there's quite a difference between the two. Short, single lane PCIe (x1) expansion cards need additional power from the computer's PSU (4 pin Molex connector in the examples below).



USB 2.0 PCI, USB 3.0 PCIe, Firewire 800 PCIe controllers (left to right)
USB 2.0 vs USB3
Mostly audio interfaces are USB 2.0, however since USB 3.0 is backwards compatible it doesn't matter in terms of audio performance. Portable HDDs are often USB 3.0 and plugging them to USB 3.0 is beneficial.

Portable USB 3.0 HDD
Laptop - Express Card vs PCMCIA
Express Card replaced PCMCIA and both are standards for notebook expansion cards. There are different sizes. You can get Express Card/PCMCIA Firewire and USB controllers but there has to be an Express Card/PCMCIA slot in your laptop.
Wireless network
Using wireless network has negative impact on audio performance. Laptops have switches that allow you to quickly disable the adapter. With desktops it's probably best not to install wireless adapters. Both desktops and laptops have regular LAN connectors.
Back to topPSU
For desktops there are online power supply unit wattage calculators and it's a good idea to use one before you choose. The more efficient and silent the PSU, the better. It's safe to go with a quality product that has all sorts of protections and temperature controlled fan speed. Especially in summer low budget PSUs fail more likely and can damage other components. Modular PSUs have detachable cable systems and removing unused cables can improve airflow. Desktop units always use the grounding pin.
Not every notebook power supply unit has the grounding pin, but it's sometimes possible to buy a replacement unit that uses one.
Back to topCASE
Of course you can buy any case that'll fit your components and it'll work, but if you want to build a cool, quiet and easy to use PC, read on.
Features
It's a matter of the looks, quiet operation and good airflow for keeping the temperature inside cool. Keep in mind that warm air rises. These are some good chassis features:
- quality material, so it doesn't resonate with cooling fans
- bottom-mounted PSU that makes the PSU draw cool air from outside of the chassis
- front panel fan with intake
- side panel exhaust
- good airflow with top exhaust
- dust filters
- SSD bay if you'd like to use one, it's not necessary because you can also buy 2.5" to 3.5" adapter bracket
- front panel USB ports
FORM FACTORS
The most popular form factor is Mid-Tower. Watch out for small and unusual form factors because not all expansion cards fit those. Only certain expansion cards come with slim bracketsa and are short enough to fit small form factor cases.


Slim bracket for Digitus Firewire 800 PCIe controller (left) and Cooler Master Elite K350 Mid-Tower computer case (right)
Back to topExamples
Here are some examples of PC configurations.
Basic #1
Recording amps and effects processors, using software drummer and perhaps a piano at the same time. It will do fine with Line 6 POD Studio interfaces. Quiet. CPU fan and PSU fan make just two.
- Intel Pentium G3220
- Intel H81M based mainboard, DVI, USB 3.0, 1 x PCI, 2 x PCIe x1, 1x PCIe x16
- Intel HD Graphics
- 1x 4GB DDR3 1333MHz
- 1TB 7200rpm HDD
- Basic Mid-Tower case
- Chieftec 350W PSU
Basic #2
Better low latency performance, enough memory to handle more than one or two software instruments. Quiet as well, because of graphics card with passive cooling.
- Intel Pentium G3220
- Intel H81M based mainboard with DVI, 2 x USB 3.0, 1 x PCI, 2 x PCIe x1, 1x PCIe x16
- AMD HD6450 with passive cooling
- 2 x 4GB DDR3 1333MHz (Dual Channel)
- 1TB 7200rpm HDD
- Cooler Master K350 case
- Chieftec 400W 80+ PSU
Performance #1
Fantastic low latency performance, fast audio and video rendering times. Powerful CPU and decent GPU.
- Intel Core i5-4460
- Intel H81M based mainboard
- AMD Radeon HD7770
- 2 x 8GB DDR3 1600MHz CL9 (Dual Channel)
- 2 x 1TB 7200rpm HDD
- Cooler Master K350 case
- XFX 450W PSU
Performance #2
High end configuration with overlocking capabilities and a SSD drive for operating system and programs. Louder and faster. Silencing computers is a topic of its own.
- Intel Pentium i5-4670K
- Intel Z87 based mainboard
- AMD Radeon R9 280 3GB GDDR5
- 2 x 8GB DDR3 2400MHz CL10 (Dual Channel)
- 256GB SSD + 1TB 7200rpm HDD
- Cooler Master Hyper EVO 212 CPU cooler
- Cooler Master K350 case
- XFX ProSeries 80+ 650W PSU
Insane #1
Dual Intel XEON, 32GB RAM, 2 x 256GB SSD in RAID...
Back to topGlossary
- AIO computer - All-In-One computer, it's a computer and a display in one, it looks like a display, it requires external keyboard and mouse
- BIOS - Basic Input Output System, simple interface that gives you access to mainboard firmware so that you can change its settings, you access it by hitting del or F2 after turning on the computer
- CL - CAS (Column Address Strobe) Latency, delay in time between the moment memory controller asks memory module for access its column and the moment the requested data is ready on the module's output
- CPU - Central Processing Unit, it's a small chip that processes program instructions and its architecture and clock speed have big impact on computer performance
- DAW - Digital Audio Workstation, it usually refers to complex music production software, in broader meaning it's the software and all the hardware used for music production (computer, audio interface, music production software)
- DIMM - Dual In-line Memory Module, it's a module that comprises of RAM circuits
- DPC - Deffered Procedure Call, mechanism in Windows that allows high-priority tasks to postpone other tasks for later execution
- DVI - Digital Visual Interface, video display interface that can be configured to DVI-D (digital), DVI-A (analog), DVI-I (digital-to-analog) modes; compatible with VGA
- DisplayPort - digital display interface, it's backwards compatible with VGA and DVI but you have to use adaptors; it can transfer audio, USB and other forms of data
- ECC - Error-correction Code, it allows detection and correction of most common data corruption, ECC memory is used in servers, financial and scientific computing, some people use it in DAWs
- Express Card - succesor of PCMCIA, expansion card standard for notebooks
- Firmware - basic software embedded in hardware
- GPU - Graphics Processing Unit, processor that calculates 2D/3D graphic effects
- HDCP - High Definition Content Protection, technology that protects digital content from being recorded
- HDD - Hard Disk Drive, device that stores data persistently on magnetic rotating disks
- HDMI - High-Definition Multimedia Interface, it's an interface for transferring video and audio
- Hyper Threading - technology introduced by Intel; in practice it makes each CPU core behave a little bit like two cores and this leads to better performance depending on the application's code
- Latency - delay, read more here
- OS - Operating System, Windows, Linux, OS X... This is the software that lets you to install and run programs, sort of a host
- Overclocking - making a component operate faster by adjusting relevant parameters such as clock speed, multiplier, voltage
- PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect, expansion card standard present to this day in some desktop motherboards
- PCIe - PCI-Express, contemporary expansion card standard for desktop computers
- PCMCIA - Personal Computer Memory Card International Association, standard for expansion cards for laptops
- PSU - Power Supply Unit, in a desktop computer this is the part which connected to the electrical outlet supplies power to other computer components, usually it's a small metal box with that's inside the computer
- RAID - Redundand Array of Independent Disks, data storage technology that combines dwo drives into one logical drive to improve performance or for data safety reasons
- RAM - Random Access Memory, fast access memory circuits that operating system and programs use it store temporary data
- SODIMM - Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module, it's a smaller DIMM for notebooks
- SSD - Solid State Drive, alternative to HDDs, it stores data persistently but instead of moving discs it uses electrical circuits
- Swap file - alternatively page file, paging file, it's a file that makes up for RAM size so that the operating system can use more memory
- TDP - Thermal Design Power, this reffers to the amount of heat generated by CPU
- Turbo Boost - CPU capability to boost clock speed of one of its cores while reducing clock speeds of other cores to perform better in single core application while maintaining its heat generation at the same level
- UEFI - Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, it's meant to replace BIOS, it defines a software interface between OS and platform firmware
- USB - Universal Serial Bus, popular standard of communication between computers and other devices
- VGA - Video Graphics Array, an analog computer display standard, also the 15-pin D-Sub display connector and the resolution of 640x480
- XMP - Intel Extreme Memory Profile, this allows you to safely overclock your RAM with predefined and tested profiles
- ms - milisecond, 0.001s
- µs - microsecond, that is 0.000001s
Further reading:
- DAW Components on www.steinberg.net
- Optimizing Windows Vista and Windows 7 for Music Production on www.presonus.com see Virtual Memory and ReadyBoost
- Hardware accelerating everything: Windows 8 graphics on blogs.msdn.com